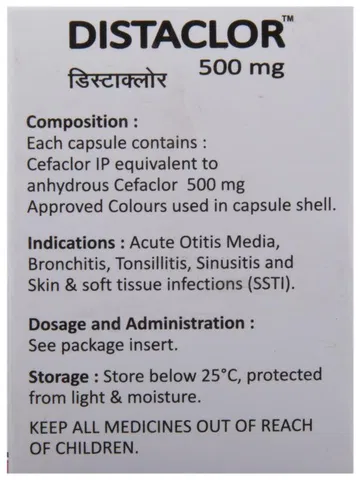
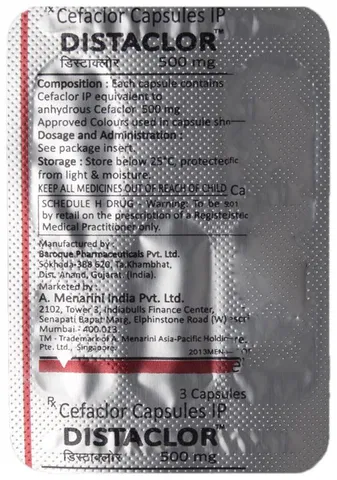
Ceclor (Cefaclor) Capsule
Generic
Cefaclor (Generic Equivalent To Ceclor)
Cefaclor (Generic Equivalent To Ceclor)
Cefaclor (Generic Equivalent To Ceclor)
Cefaclor (Generic Equivalent To Ceclor)
The most common side effects of this medicine include rash, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and changes in liver function tests. These are usually mild but let your doctor know if they bother you or last more than a few days.
Before using it, you should tell your doctor if you are allergic to any antibiotics or have any kidney or liver problems. You should also let your doctor know all other medicines you are taking as they may affect, or be affected by this medicine. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should consult their doctor before using it. Avoid consuming alcohol while taking this medicine as it may cause unpleasant side effects like nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, and palpitations.
Uses Of Ceclor Capsule
- Bacterial infections
Benefits Of Ceclor Capsule
In Bacterial Infections
Ceclor Capsule is an antibiotic medicine that works by killing the infection causing bacteria in your body. It is effective for bacterial infections of the throat, ears, urinary tract, skin, and soft tissues. This medicine usually makes you feel better within a few days, but you should continue taking it as prescribed even when you feel better. Stopping it early may make the infection come back and harder to treat.
Side Effects Of Ceclor Capsule
Most side effects do not require any medical attention and disappear as your body adjusts to the medicine. Consult your doctor if they persist or if you’re worried about them.
Common Side Effects Of Ceclor
- Rash
- Vomiting
- Allergic reaction
- Nausea
- Injection site reaction
- Increased liver enzymes
- Diarrhea
How To Use Ceclor Capsule
Take this medicine in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Ceclor Capsule may be taken with or without food, but it is better to take it at a fixed time.
How Ceclor Capsule Works
Ceclor Capsule is an antibiotic. It kills bacteria by preventing them from forming the bacterial protective covering (cell wall) which is needed for them to survive.
Disclaimer :The information provided on the website is intended to facilitate awareness about healthcare products and medical conditions generally but it is not a substitute for professional medical attention or advice. You should always speak with a qualified healthcare practitioner before taking any prescription or non-prescription drug. |
| Product Type--Salt | Generic–Cefaclor (Generic Equivalent To Ceclor), Brands–Ceclor |
|---|---|
| tag--Manufacturer | Best Selling–Sun Pharmaceutical, Top Brand–A. Menarini, Best Selling–A. Menarini, Top Brand–United Biotech, Branded–Pharma Fabrikon |
| Power--Pack Size | 250mg–6 Capsules, 250mg–12 Capsules, 250mg–24 Capsules, 250mg–48 Capsules, 250mg–10 Capsules, 250mg–20 Capsules, 250mg–40 Capsules, 250mg–80 Capsules, 500mg–6 Capsules, 500mg–12 Capsules, 500mg–24 Capsules, 500mg–48 Capsules, 500mg–8 Capsules, 500mg–16 Capsules, 500mg–32 Capsules, 500mg–64 Capsules, 500mg–10 Capsules, 500mg–20 Capsules, 500mg–40 Capsules, 500mg–80 Capsules |